Enhance Your Dental Care with Stem Cell for Teeth
Key Highlights
· Stem cell therapy offers a revolutionary approach to dental care, potentially transforming how we address tooth loss, damage, and disease.
· Stem cells, renowned for their regenerative capabilities, are being explored to regenerate dental tissues like tooth pulp, dentin, and periodontal ligaments.
· This blog post will cover the science behind stem cell therapy in dentistry, exploring the types of dental stem cells, their applications, and the process involved in harnessing their potential.
· We'll also discuss this field's exciting future and address common questions and concerns about its safety and efficacy.
· Stay informed about this cutting-edge technology and how it might revolutionize your dental health journey.
Introduction
Imagine a future where losing teeth or having damaged ones is not scary. Discoveries in stem cell research are giving us hope for better dental health. Stem cells can make more of themselves and change into different cell types. This ability may help fix damaged dental tissues and change how we care for our teeth.
Understanding Stem Cell Therapy in Dentistry
Stem cell therapy is changing many areas of medicine, including dentistry. This amazing method uses the body's natural ability to heal itself. It helps to fix damaged tissues and improve oral health.
The main part of this therapy is stem cells. These are special cells that can turn into different types of cells. In dentistry, these cells can help repair important parts like dentin, the tough tissue under the tooth enamel. They can also help to rebuild cementum, the outer layer of the tooth root, and periodontal ligaments that connect the teeth to the jawbone. In some cases, they can even help grow new teeth.
The Science Behind Stem Cells for Dental Care
The dental pulp is the soft part inside our teeth, which contains nerves and blood vessels. It is a valuable source of stem cells called dental pulp stem cells. These special cells can turn into different dental tissues, which makes them great for regenerative therapies.
When we have dental damage or disease, these stem cells can respond to signals around them. They release growth factors that help create new tissue. This complex process usually uses biocompatible scaffolds and matrices. These items help with tissue engineering in dentistry.
Scientists are looking for ways to effectively isolate, grow, and transplant these cells. They are working on creating biocompatible scaffolds to help guide tissue growth and improve cell delivery methods. The area of stem cell-based dental care is growing quickly.
Evolution of Stem Cell Use in Dental Treatments
The use of stem cells in dentistry is still new, but there have been some promising developments in recent years. Pre-clinical studies, mainly done on animals, show that stem cells can help regenerate dental tissues.
Several clinical trials are in progress to check how safe and effective these treatments are for people. Researchers are looking into different uses, like fixing pulp in decayed teeth, repairing the periodontal ligament in severe periodontitis, and even creating whole teeth.
As these regenerative therapies improve and clinical studies continue, stem cell-based treatments offer great hope. They could change the dental field and provide long-lasting solutions for various dental health issues.
The Role of Stem Cells in Tooth Regeneration
Tooth loss happens because of severe decay, injury, or periodontal disease. People usually deal with this by using artificial teeth like dentures, bridges, and implants. Now, stem cell technology could change all that.
Stem cells can turn into different cell types needed for teeth. They may help regain lost or damaged parts of teeth, like the enamel, dentin, cementum, and even the pulp. This exciting possibility opens the door for a future where tooth regeneration is a real option.
How Stem Cells Can Promote Tooth Healing and Regrowth
Tooth regeneration is a complex process. Different types of cells need to work together. Dental stem cells are found in places like dental pulp, periodontal ligaments, and even baby teeth. These cells have great potential for helping in tooth regeneration.
When placed in the right environment, they can change into the specific cell types needed, like ameloblasts for forming enamel, odontoblasts for creating dentin, and cementoblasts for making cementum.
This process of changing into the right cells is guided by signaling molecules and growth factors. This guidance can help make new tooth structures and restore healthy, functional teeth.
Breakthroughs in Tooth Regeneration Techniques
Recent progress in growing new teeth, especially whole ones, excites dentistry. Scientists aim to steer stem cells toward making working teeth.
A study in the dental journal showed success in regrowing tooth ligaments using stem cells. These special cells from around teeth fix damaged ligaments and help reattach teeth.
Types of Dental Stem Cells and Their Applications
Dental tissues have different types of stem cells. Each type has special features and helpful benefits. Dental pulp stem cells are located in the tooth's pulp chamber. They are easy to reach and can change into many cell types.
Periodontal ligament stem cells are found in the tissues that support tooth roots. They are important for helping teeth attach and grow back. Also, stem cells from baby teeth and wisdom teeth are useful. They can be used for different dental and medical purposes.
Exploring Different Sources of Dental Stem Cells
The search for easy and effective sources of dental stem cells has led researchers to check out different options. Baby teeth, which we often throw away after they fall out, have a good supply of stem cells called SHED (Stem cells from Human Exfoliated Deciduous teeth).
Wisdom teeth, removed for braces or to stop problems, also have many stem cells. These cells can turn into different cell types and have great potential for different uses in dental care.
Even extracted adult teeth have some stem cells, though not as many as baby or wisdom teeth. They can still be useful in certain situations. As research continues, these different stem cell sources give us exciting personal dental care opportunities.
Innovative Applications of Stem Cells in Dentistry
Stem cells have great potential for growing new teeth and helping with many dental health problems. Here are some creative uses that people are looking into:
· Treating Periodontal Disease: Stem cells might help heal damaged gum and bone tissue. This could reverse damage from periodontal disease and improve gum health.
· Improving Dental Implants: Using stem cells in dental implants may help them bond better to the jawbone. This could lead to higher success rates for implants.
· Regenerating Bone Loss: Stem cells can help rebuild bone in cases of jawbone loss. This creates a stronger base for dental implants or other dental work.
These new ways to use stem cells show a big change in dentistry. We are moving from traditional methods to new solutions that help the body heal and grow naturally.
The Process of Dental Stem Cell Therapy
Dental stem cell therapy starts by carefully taking out or collecting tissues with many stem cells. These include dental pulp from pulled teeth or tissue from the periodontal ligament. These tissues are processed in a lab to separate and grow the needed stem cells.
After gathering enough cells, we can use them immediately or store them in a freezer for later use. How we deliver the cells and the treatment plan will vary based on the dental problem we are treating.
From Extraction to Preservation: A Step-by-Step Guide
Successfully using dental stem cells for treatments involves careful steps from extraction to storage. Here is a simple guide to the main stages:
- Tooth Extraction: When a tooth is removed, like a baby tooth, wisdom tooth, or an adult tooth, due to damage or decay, it can still be helpful. Instead of throwing it away, you can send it to a dental stem cell bank.
- Stem Cell Isolation: In the lab, dental pulp stem cells are removed from the tooth’s inner part, called the pulp chamber. This process doesn’t hurt the tooth and helps obtain the most healthy stem cells possible.
- Cryopreservation: The stem cells are frozen to keep them alive for a long time. These stored cells can be thawed and used for dental treatments when needed.
This careful process allows people to keep their own strong stem cells for possible dental therapies when needed.
Integrating Stem Cells into Dental Practices
Translating new stem cell research into everyday dental care is crucial for improving dental services. Places like Columbia University Medical Center in New York lead this effort. They connect scientific findings with real-world use.
Dentists are now adding stem cell treatments to their practices. This provides new options for different dental issues. Many dental experts work with labs that can handle and keep dental mesenchymal stem cells.
This teamwork helps patients who decide to bank their stem cells. They can access these regenerative therapies when necessary. As this field grows, we will likely see stem cell therapies become more common in regular dentistry.
Benefits of Stem Cell Therapy for Dental Health
Stem cell therapy has many benefits for dental health. It helps address the main problems behind dental issues and supports lasting oral health. Unlike regular treatments that mainly manage symptoms, stem cell therapies work to rebuild damaged tissues and bring back normal function.
These therapies use the body’s natural healing powers. They offer a new way to treat tooth decay, gum disease, and loss. This method opens the door to better and healthier dental care in the future.
Potential for Lifelong Dental Health Improvements
Stem cell therapy has a great chance to change dental care and improve our dental health for life. Using the body’s ability to heal, these therapies might fix dental problems right at their source.
Fixing missing teeth with natural regenerated teeth could be possible. This means no more need for artificial teeth, and it helps keep the jawbone strong. The benefits can go beyond looks to better oral health and useful restoration.
Think about a future where we can fix damaged tissues, fight gum disease directly, and keep our smiles healthy for many years. Even though more research and tests are needed, stem cell-based dental therapy's future looks promising.
How can stem cells be used in dental procedures?
Stem cells can be utilized in dental procedures to regenerate tissues like teeth, gums, and jawbones. This innovative approach involves harvesting stem cells from a patient's body and applying them to promote natural healing and regeneration, improving oral health outcomes.
Conclusion
In conclusion, stem cell therapy in dentistry is stimulating. It brings new hope for better dental health and treatments that can help the body heal itself. Learning about how teeth can regenerate and how dental stem cells can be used shows how dental practices are changing. By looking at different places to get stem cells and new methods, the future of dental care seems bright. Using stem cell therapy can help with healing and regrowth. It can also lead to better dental health for a lifetime. With progress in tooth regeneration, using stem cells in dental practices could change how we care for our teeth. Start improving your dental health by exploring stem cell therapy's easy benefits.
Frequently Asked Questions
How Safe Is Stem Cell Therapy for Teeth?
Clinical studies show that stem cell therapy is usually safe. This method often uses the tooth pulp from the patient. This reduces worries about rejection or negative reactions with foreign cells or materials. More research and ongoing checks by groups like the FDA will give us better safety information.
stem cell for teeth stem cell for teeth stem cell for teeth stem cell for teeth
stem cell for teeth stem cell for teeth human teeth root canal regenerative medicine cord blood body’s stem cells tooth damage oral cavity human dental pulp stem cells dental pulp tissue bone marrow spinal cord injuries living stem cells years of age tissues of the neural stem cells heart disease drug administration stem cell for teeth stem cell for teeth stem cell for teeth
https://www.nymedicalmarketing.com
https://cta-redirect.hubspot.com/cta/redirect/4853756/462f8ab0-fde0-471e-a4ba-82d5c9903815
https://www.dmca.com/Protection/Status.aspx
https://www.aaid.com/about/Press_Room/History_and_Background.html

Slide title
Write your caption hereButton
Slide title
Write your caption hereButton
Slide title
Write your caption hereButton
Slide title
Write your caption hereButton
Slide title
Write your caption hereButton
Slide title
Write your caption hereButton
Slide title
Write your caption hereButton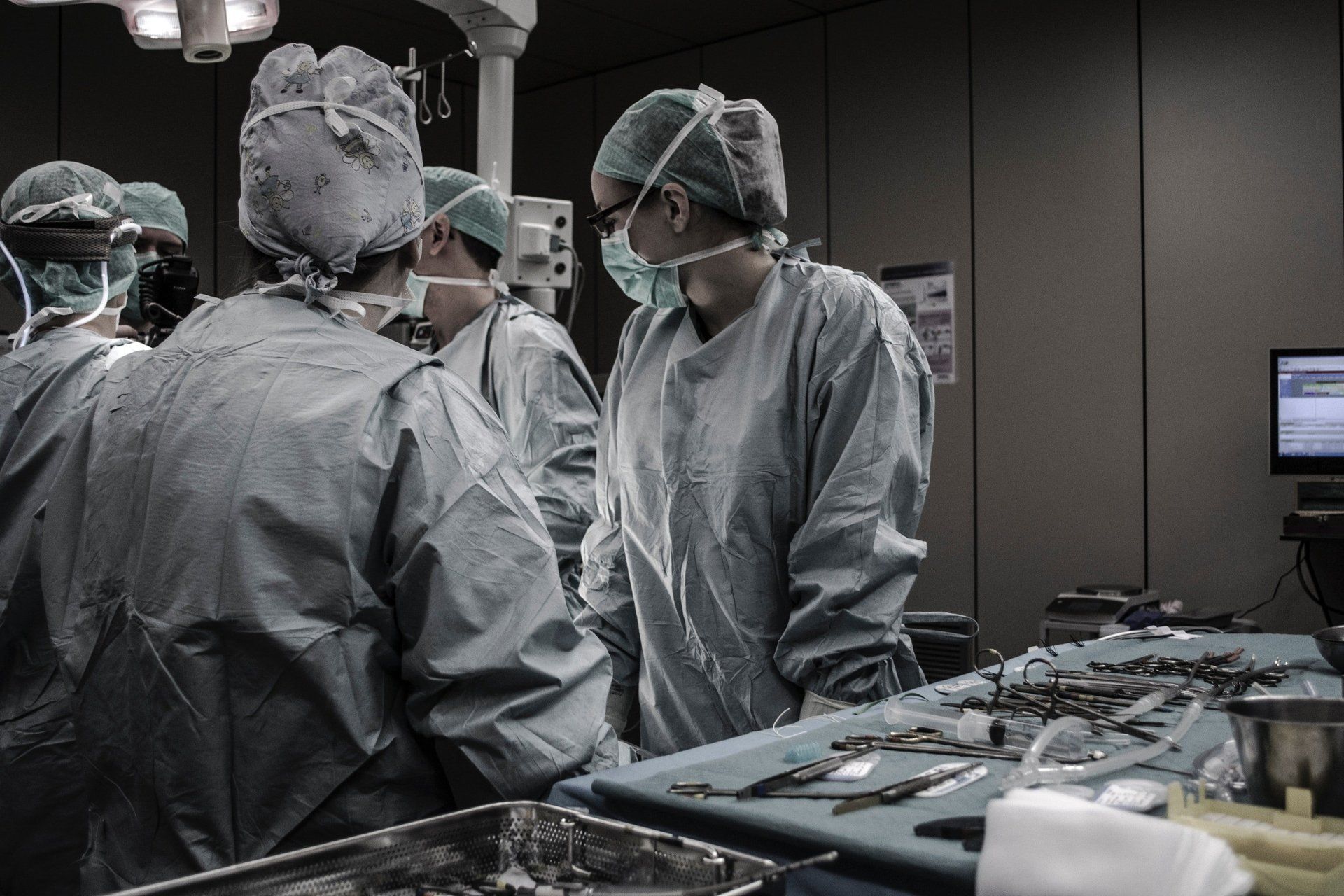
Slide title
Write your caption hereButton
Slide title
Write your caption hereButton
Slide title
Write your caption hereButton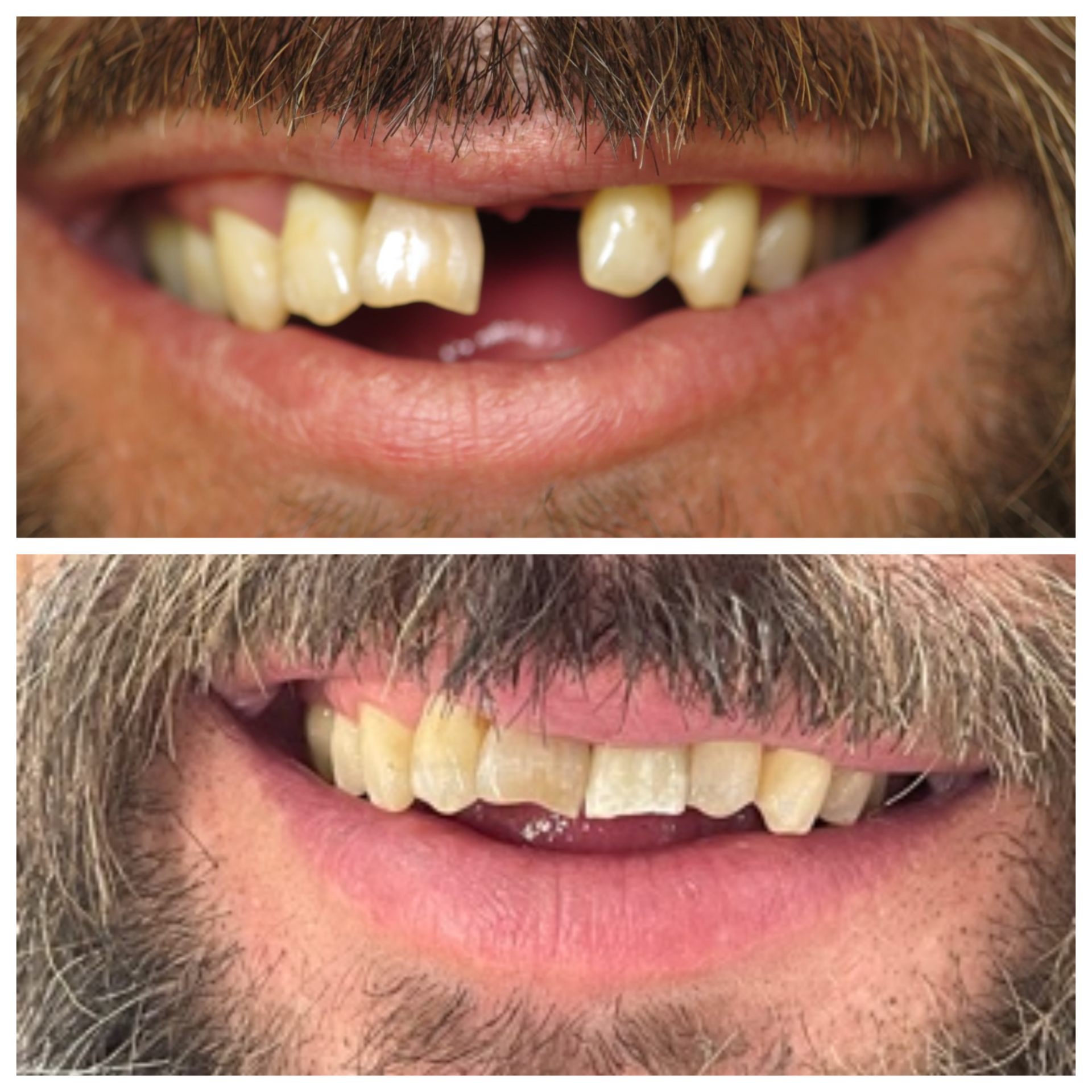
Slide title
Write your caption hereButton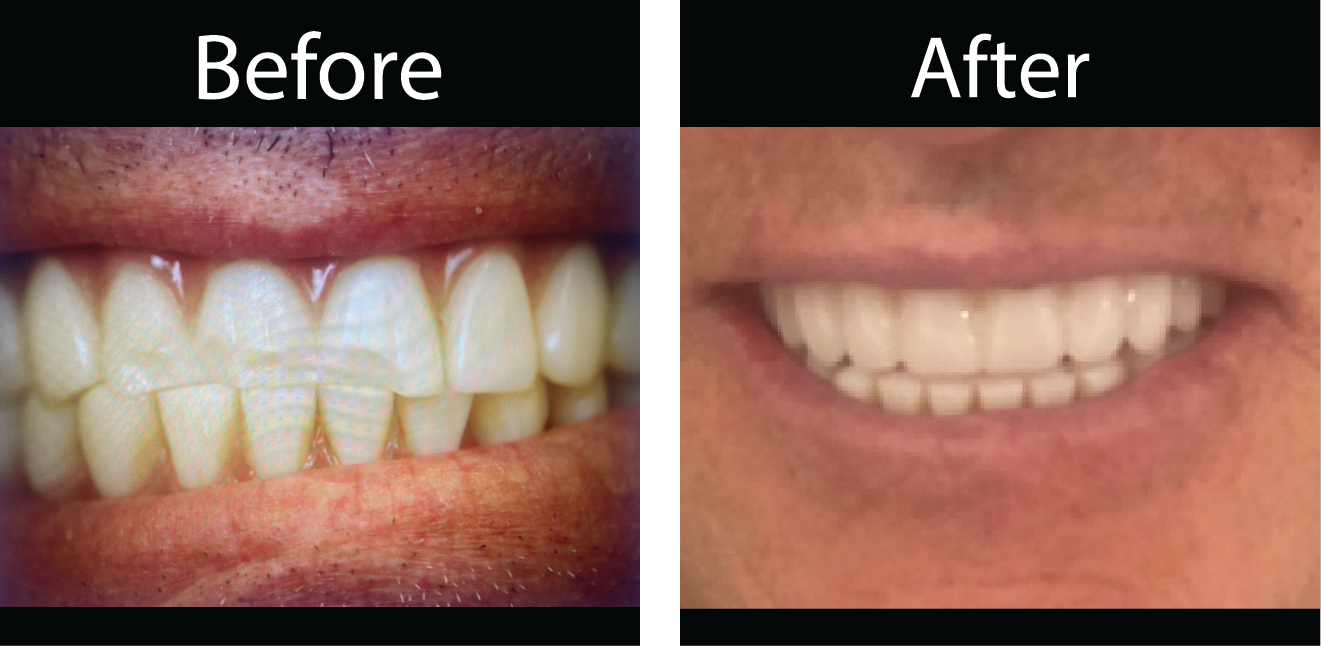
Slide title
Write your caption hereButton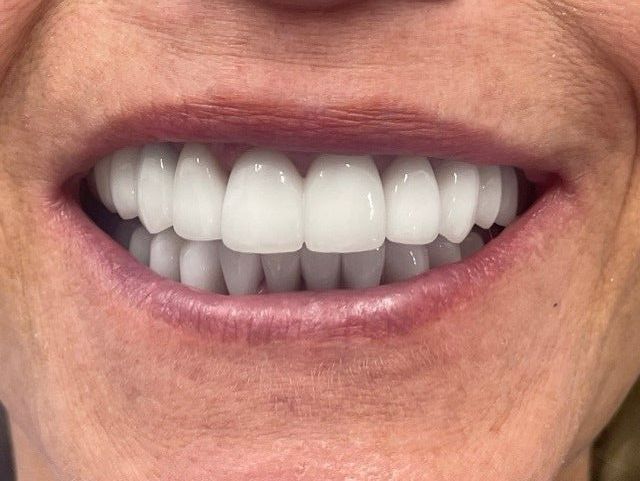
Slide title
Write your caption hereButton
Slide title
Write your caption hereButton
Slide title
Write your caption hereButton
Slide title
Write your caption hereButton
Slide title
Write your caption hereButton
Slide title
Write your caption hereButton
Slide title
Write your caption hereButton
DR. KONSTANTINOS HAROGIANNIS, DDS
What is the difference between a dentist and a cosmetic dentist?
Please feel free to call us to schedule visit with Dr. Harogiannis
303 - 789 - 2020Monday – Thursday: 7:30am to 5:00pm
Fridays: Appointments available upon request
Saturday - Sunday: Closed
3575 S Sherman St Suite #3 Englewood, CO 80113
Call us: 303-789-2020
Monday – Thursday: 7:30am to 5:00pm
Friday – Saturday: Appointments available upon request
Sunday: Closed
3575 S Sherman St Suite #3
Englewood, Colorado 80113
Call us: 303-789-2020
